The Oceans - Ice in Arctic Ocean and Southern Ocean - what's happening?
Ice, water and water vapour - the three states of H2O....solid, liquid and gas.
The Earth has all three, which is unusual.
Planets are usually too hot or too cold to have them all.
Planets are usually too hot or too cold to have them all.
Ice on Earth is melting.
The Earth's poles are warming faster than the rest of the planet.
The Earth's poles are warming faster than the rest of the planet.

The Arctic includes an ocean covered by sea ice.
Arctic Ocean sea ice melts in Summer and then refreezes in Winter.
Arctic Ocean sea ice melts in Summer and then refreezes in Winter.
The area of Arctic sea ice is largest in March each year, and at its lowest each September.
It is reducing over time - the graph comes from the US National Snow and Ice Data Center.

One reason is that energy is carried to the poles by large weather systems.
Antarctica is a continent covered by ice, unlike the ocean in the Arctic.
The sea ice in the Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica melts almost to the coast each summer.
The winter sea ice has increased by around 1 % over the last few decades.

Here is an outline of what is happening in the seas around Antarctica.
Seawater does not freeze until around minus 2 degrees C because it is salty.
Seawater does not freeze until around minus 2 degrees C because it is salty.
This effect of salt, of course, is used to help defrost roads.
The meltwater off Antarctica’s ice sheets is freshwater.
Freshwater has a low density, so it forms a layer on top of the sea.
Freshwater freezes (of course) at zero degrees C.

So the top layer freezes more easily.

So the top layer freezes more easily.
Also windchill helps to freeze that top layer.

Professor Helen Fricker and colleagues at Scripps Institution of Oceanography have used two decades of data from European radar satellites to compile an assessment of Antarctica's floating ice shelves.
In the first decade, the total losses from the ice shelves averaged 25 cubic km per year.
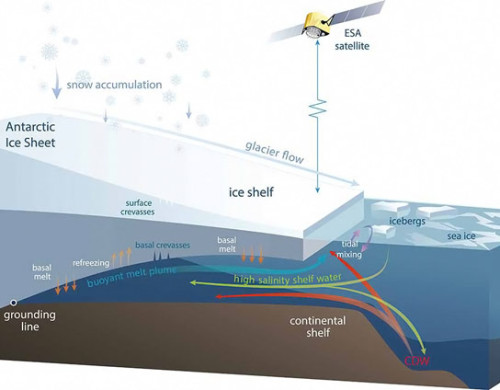
But during the second decade, this had jumped to 310 cubic km per year.
"For before 2003, ice-shelf volume for all Antarctica did not change much," said Fernando Paolo, one of the team.
"Since then, volume loss has been significant. The western ice shelves have been persistently thinning for two decades, and earlier gains in the eastern ice shelves ceased in the most recent decade," he told BBC News.

